Configuration and Administration Tools Overview
This chapter introduces the various administration tools
of Oracle Net Services. It discusses the main administration
application, Oracle Net Manager, and describes how to launch and
navigate through it. It also introduces the command line control
utilities.
This chapter contains these topics:
- Oracle Net Manager
- Oracle Net Configuration Assistant
- Oracle Net Control Utilities
- Duties of a Network Administrator
Oracle Net Manager
Oracle Net Manager
is a graphical user interface tool that combines configuration
abilities with Oracle Names component control to provide an integrated
environment for configuring and managing Oracle Net. It can be used on
either the client or server. Oracle Net Manager is also integrated with
Oracle Enterprise Manager.
You can use Oracle Net Manager to configure the following network components:
- Naming--Define simple names, connect identifiers, and map them to connect descriptors
to identify the network location and identification of a service.
Oracle Net Manager supports configuration of connect descriptors in
local
tnsnames.orafiles, a centralized LDAP-compliant directory service, or an Oracle Names server. - Naming Methods--Configure the different ways in which connect identifiers are resolved into connect descriptors.
- Profiles--Configure preferences for enabling and configuring Oracle Net features on the client or server.
- Listeners--Create and configure listeners to receive client connections.
If an Oracle Names server is configured, you can start, stop, tune, or gather statistics for it with Oracle Net Manager.
This section introduces you to the features of Oracle Net
Manager. However, the primary documentation for using Oracle Net Manager
is the accompanying online help. This section contains these topics:
Starting Oracle Net Manager
You can start Oracle Net Manager using the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console or as an independent application.
To start Oracle Net Manager from the Oracle Enterprise Manager console, on the Oracle Enterprise Manager console, choose Tools > Service Management > Oracle Net Manager.
To start Oracle Net Manager as standalone application:
- On UNIX, run
netmgrfrom$ORACLE_HOME/bin - On Windows NT, choose Start > Programs > Oracle - HOME_NAME > Configuration and Migration Tools > Net Manager
Navigating Oracle Net Manager
The Oracle Net Manager interface includes two panes, a toolbar, and various menu items.
Figure 5-1 Oracle Net Manager Interface
Panes
The Oracle Net Manager interface has two panes: the navigator pane and the right pane.
Navigator Pane
The navigator pane provides a graphical tree view of
network objects and the objects they contain, organized in hierarchies
of folders. You can use the navigator pane to view, modify, add, or
delete objects in each folder.
The navigator pane functions the same way as it does in
other Oracle Enterprise Manager applications. That is, the navigator
pane lets you:
- Expand and contract folders so that you can navigate to the network object you want to monitor or manage. Examples of objects are connect identifiers, listeners, profiles, and Oracle Names servers.
- Right-click an object to perform operations on the object.
When you expand a folder, you see a nested list of objects
and folders. When a object is selected, information about the object is
displayed in the right pane of the Oracle Net Manager.
Table 5-1 lists the main folders in the navigator pane.
Table 5-1 Oracle Net Manager Navigator Pane Folders
Right Pane
The right pane contains property sheets that enable you to configure network components. Figure 5-2 shows the Service Attributes property sheet used for connect identifier configuration.
Figure 5-2 Service Attributes Property Sheet
Toolbar
The toolbar contains buttons that correspond to the
network objects in the folder hierarchies. The toolbar buttons are
enabled depending on the objects viewed or selected in a pane. Move the
mouse cursor over a toolbar button to display the description of the
button's function. The toolbar buttons are:
Create
This button creates new connect identifiers, listeners, and Oracle Names servers objects under the Directory or Local > Service Naming, Listeners, and Oracle Names Servers folders.
Delete
This button deletes connect identifier and listener objects under the Directory or Local > Service Naming and Listeners folders.
Verify Connectivity
This button verifies the connectivity of a selected
connect identifier to an Oracle database service. During a connectivity
test, a connection to a database service is made by using connect
descriptor information stored in a directory server or a
tnsnames.ora file.Help
The Help button opens the Oracle Net Manager online help.
Menus
You use Oracle Net Manager menus to perform actions, such
as testing connectivity to an Oracle database, and to open wizards and
dialog boxes. The following list describes the items available under
each menu.
File Menu
Table 5-2 File Menu Contents
Edit Menu
Table 5-3 Edit Menu Contents
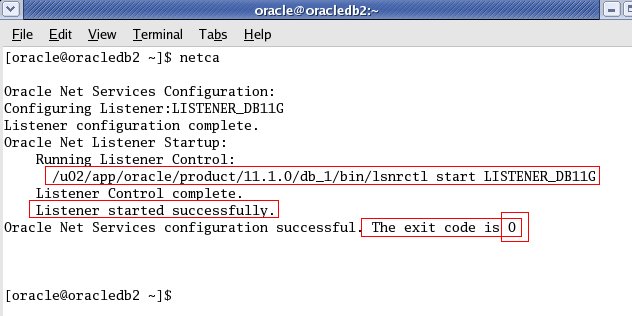
netca (Listener Configuration for Oracle 11g Database
Sometimes you need to run netca manually to configure Listener for your
database. In Oracle 11g i found this message as a warning when selecting
Database Control Configuration.
 So planned to document this and of course this is one of the part of Oracle 11g Installation.
So planned to document this and of course this is one of the part of Oracle 11g Installation.
1. Open a terminal as a Oracle user and run netca.
Select -> Listener Configuration
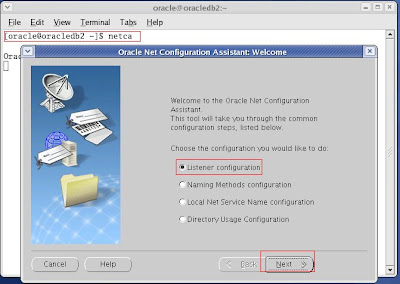 2. Select Add,
as we are going to create a LISTENER for a new setup. If we have any
existing listener running on the Server, remain options will be
highlight like "delete" "re-configure" etc.
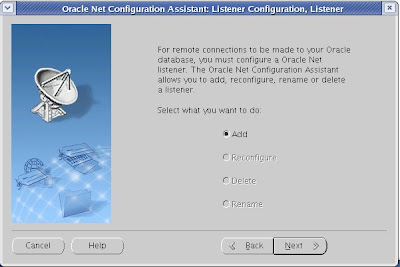
2. Select Add,
as we are going to create a LISTENER for a new setup. If we have any
existing listener running on the Server, remain options will be
highlight like "delete" "re-configure" etc.
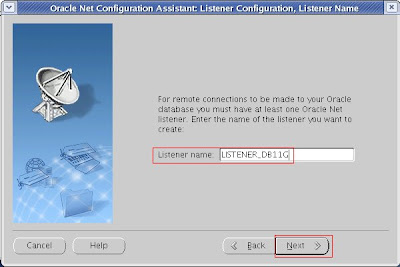
 3. Listener Name, or you can leave the existing one.
3. Listener Name, or you can leave the existing one.
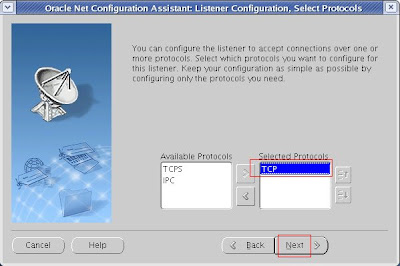
 4. TCP is selected as default.
4. TCP is selected as default.
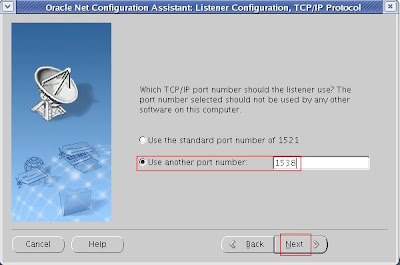
 5. Select the Port here (or) you can leave the default port.
5. Select the Port here (or) you can leave the default port.
 Starting up and shutting down the oracle listener is a routine task
for a database administrator. However a Linux system administrator or
programmer may end-up doing some basic DBA operations on development
database. It is critical for non-DBAs to understand the basic database
admin activities.
Starting up and shutting down the oracle listener is a routine task
for a database administrator. However a Linux system administrator or
programmer may end-up doing some basic DBA operations on development
database. It is critical for non-DBAs to understand the basic database
admin activities.
In this article, let us review how to start, stop, check status of an oracle listener using Oracle listener control utility LSNRCTL.
If the Oracle listener is not running, you’ll get the following message.
If the Oracle listener is running, you’ll get the following message.
 So planned to document this and of course this is one of the part of Oracle 11g Installation.
So planned to document this and of course this is one of the part of Oracle 11g Installation.1. Open a terminal as a Oracle user and run netca.
Select -> Listener Configuration
 2. Select Add,
as we are going to create a LISTENER for a new setup. If we have any
existing listener running on the Server, remain options will be
highlight like "delete" "re-configure" etc.
2. Select Add,
as we are going to create a LISTENER for a new setup. If we have any
existing listener running on the Server, remain options will be
highlight like "delete" "re-configure" etc. 3. Listener Name, or you can leave the existing one.
3. Listener Name, or you can leave the existing one. 4. TCP is selected as default.
4. TCP is selected as default. 5. Select the Port here (or) you can leave the default port.
5. Select the Port here (or) you can leave the default port.

 Starting up and shutting down the oracle listener is a routine task
for a database administrator. However a Linux system administrator or
programmer may end-up doing some basic DBA operations on development
database. It is critical for non-DBAs to understand the basic database
admin activities.
Starting up and shutting down the oracle listener is a routine task
for a database administrator. However a Linux system administrator or
programmer may end-up doing some basic DBA operations on development
database. It is critical for non-DBAs to understand the basic database
admin activities. In this article, let us review how to start, stop, check status of an oracle listener using Oracle listener control utility LSNRCTL.
How To Start, Stop and Restart Oracle Listener
Oracle Listener Status
Before starting, stopping or restarting make sure to execute lsnrctl status command to check the oracle listener status as shown below. Apart from letting us know whether the listener is up or down, you can also find the following valuable information from the lsnrctl status command output.- Listner Start Date and Time.
- Uptime of listner – How long the listener has been up and running.
- Listener Parameter File – Location of the listener.ora file. Typically located under $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin
- Listener Log File – Location of the listener log file. i.e log.xml
If the Oracle listener is not running, you’ll get the following message.
$ lsnrctl status LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on 04-APR-2009 16:27:39 Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) TNS-12541: TNS:no listener TNS-12560: TNS:protocol adapter error TNS-00511: No listener Linux Error: 111: Connection refused Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=IPC)(KEY=EXTPROC))) TNS-12541: TNS:no listener TNS-12560: TNS:protocol adapter error TNS-00511: No listener Linux Error: 2: No such file or directory
If the Oracle listener is running, you’ll get the following message.
$ lsnrctl status LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on 04-APR-2009 16:27:02 Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) STATUS of the LISTENER ------------------------ Alias LISTENER Version TNSLSNR for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production Start Date 29-APR-2009 18:43:13 Uptime 6 days 21 hr. 43 min. 49 sec Trace Level off Security ON: Local OS Authentication SNMP OFF Listener Parameter File /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/network/admin/listener.ora Listener Log File /u01/app/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/devdb/listener/alert/log.xml Listening Endpoints Summary... (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=EXTPROC))) Services Summary... Service "devdb" has 1 instance(s). Instance "devdb", status UNKNOWN, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "devdb.thegeekstuff.com" has 1 instance(s). Instance "devdb", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "devdbXDB.thegeekstuff.com" has 1 instance(s). Instance "devdb", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... Service "devdb_XPT.thegeekstuff.com" has 1 instance(s). Instance "devdb", status READY, has 1 handler(s) for this service... The command completed successfully
2. Start Oracle Listener
If the Oracle listener is not running, start the listener as shown below. This will start all the listeners. If you want to start a specific listener, specify the listener name next to start. i.e lsnrctl start [listener-name]$ lsnrctl start LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on 04-APR-2009 16:27:42 Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. Starting /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/bin/tnslsnr: please wait... TNSLSNR for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production System parameter file is /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/network/admin/listener.ora Log messages written to /u01/app/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/devdb/listener/alert/log.xml Listening on: (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) Listening on: (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=EXTPROC))) Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) STATUS of the LISTENER ------------------------ Alias LISTENER Version TNSLSNR for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production Start Date 04-APR-2009 16:27:42 Uptime 0 days 0 hr. 0 min. 0 sec Trace Level off Security ON: Local OS Authentication SNMP OFF Listener Parameter File /u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.0/network/admin/listener.ora Listener Log File /u01/app/oracle/diag/tnslsnr/devdb/listener/alert/log.xml Listening Endpoints Summary... (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=ipc)(KEY=EXTPROC))) Services Summary... Service "devdb" has 1 instance(s). Instance "devdb", status UNKNOWN, has 1 handler(s) for this service... The command completed successfully
3. Stop Oracle Listener
If the Oracle listener is running, stop the listener as shown below. This will stop all the listeners. If you want to stop a specific listener, specify the listener name next to stop. i.e lsnrctl stop [listener-name]$ lsnrctl stop LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on 04-APR-2009 16:27:37 Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) The command completed successfully
4. Restart Oracle Listener
To restart the listener use lsnrctl reload as shown below instead of lsnrctl stop and lsnrctl start. realod will read the listener.ora file for new setting without stop and start of the Oracle listener.$ lsnrctl reload LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on 04-APR-2009 17:03:31 Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. Connecting to (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=192.168.1.2)(PORT=1521))) The command completed successfully
Available Listener Commands
lsnrctl help command will display all available listener commands. In Oracle 11g following are the available listener commands.- start - Start the Oracle listener
- stop - Stop the Oracle listener
- status - Display the current status of the Oracle listener
- services - Retrieve the listener services information
- version - Display the oracle listener version information
- reload - This will reload the oracle listener SID and parameter files. This is equivalent to lsnrctl stop and lsnrctl start.
- save_config – This will save the current settings to the listener.ora file and also take a backup of the listener.ora file before overwriting it. If there are no changes, it will display the message “No changes to save for LISTENER”
- trace - Enable the tracing at the listener level. The available options are ‘trace OFF’, ‘trace USER’, ‘trace ADMIN’ or ‘trace SUPPORT’
- spawn - Spawns a new with the program with the spawn_alias mentioned in the listener.ora file
- change_password – Set the new password to the oracle listener (or) change the existing listener password.
- show - Display log files and other relevant listener information.
$ lsnrctl help LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on 04-APR-2009 16:12:09 Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. The following operations are available An asterisk (*) denotes a modifier or extended command: start stop status services version reload save_config trace spawn change_password quit exit set* show*
Get More help on Specific Listener Command
You can get detailed help on a specific oracle listener command as
shown below. In the following example, it gives all the available
arguments/parameters that can be passed to the lsnrctl show command.
$ lsnrctl help show LSNRCTL for Linux: Version 11.1.0.6.0 - Production on 04-APR-2009 16:22:28 Copyright (c) 1991, 2007, Oracle. All rights reserved. The following operations are available after show An asterisk (*) denotes a modifier or extended command: rawmode displaymode rules trc_file trc_directory trc_level log_file log_directory log_status current_listener inbound_connect_timeout startup_waittime snmp_visible save_config_on_stop dynamic_registration
No comments:
Post a Comment